
If you have not yet signed up for the ISSA CPT certification, receive a big discount here.
Get your copy of the ISSA CPT exam cheat sheet.
It helps immensely in your ability to study for the ISSA test. This PDF printable one-page sheet gives you a breakdown of the skills and knowledge candidates need to pass the exam.
My PTP students report cutting their ISSA study time and effort in half with Trainer Academy.
Benefit from the Exam Pass Guarantee and Retake Fee Guarantee. Plus, take advantage of my current discount code PTPJULY for 45% off the MVP Program (Ends July 6th, 2025).
Try it out for free here to see if it’s right for you, or read my detailed review for further insights.
1: Describe how cells and metabolism relate?
“Metabolism” is essentially the sum of all reactions that take place to build up and break down the body.
2: In what way do healthy cells positively affect us?
Healthy cells = healthy metabolism
3: Describe the following regarding how the body is organized:
Organism: The complete living being
Organ systems: The collaborative arrangement of organ function
Organs: Organised tissue systems that perform a vital function
Tissues: organized groups of cells
Cells: a single unit of contained biochemical function
Organelles: cellular constituents that collaborate toward cellular function
Chemicals: molecular substances that are used for biochemical reactions in cells
4: Describe the following functions of the body and what each of them specifically does:
enzymes: specialized proteins that catalyze metabolic function
co‐enzymes: chemical components that optimize enzyme function
protein receptors and cell signaling pathways: protein communication docking points that elicit cellular activity once in contact with relevant chemicals
transport proteins: exist in cells and act as communication mediums for processes signaled outside of cells
5: What are “soluble units,” and what is the most basic of these macronutrients?
- Protein: amino acids
- Carbohydrates: Glucose
- Fat: fatty acids
6: In what way does digestion function, and what is the process of digestion beginning with the brain?
When the brain recognizes food intake, it stimulates the release of saliva and its constituent enzymes that begin breaking down in the mouth. After that, a “bolus” of food travels down the esophagus and enters the stomach. Thanks to the brain – and the chewing – the stomach is ready with acids, mucus, and enzymes. Once chyme has entered the small intestine, the transport rate is slow, with waves of smooth muscle contracting and propelling chyme along its journey through the intestines. Once the remaining food enters the large intestine, another 12-25 hours can pass before waste products are eliminated from the body. Bacteria digest some remaining residues. As food moves into the colon, the bacteria there digest fiber, creating short-chain fatty acids, vitamin K, and more. Waste is then compacted into feces and moved toward the rectum, where it can be released through bowel movements
7: Name the digestive organs in the chart below (see Figure 15.2 (p. 524) in the textbook) and explain their function

8: Based on these major mechanics, how is food absorbed?
Simple diffusion: moving from higher to lower concentration.
Facilitated diffusion: a carrier protein helps to shuttle nutrients across the barrier from higher to lower concentration
Active transport: Active transport relies on energy and a carrier protein from lower to higher concentration.
9: What is the role of the liver in absorption? What are its four main functions?
It screens everything we swallow
lt ensures that blood sugar is balanced.
lt synthesizes proteins from the amino acids we eat.
lt can convert fatty acids into stored triglycerides.
10: What does “energy transfer” mean, and how does it occur?
Energy transfer stipulates that energy is neither created nor destroyed but rather transferred and manipulated into different states and through different pathways by different reactions. From a biochemical/food perspective, this means:
Exclusive PTP CPT Offers |
||
|---|---|---|
Most Popular Cert | Best Online NCCA Cert | Best Study Materials |
Gold Standard Cert | A Good Option | Best CPT for you?  |
- Oxidation for energy production
- Transformation and incorporation into structural components of the body
- Storage for future energy provision
- Excretion and elimination from the body
11: Describe ATP as well as the role of triglycerides and glycogen in ATP synthesis
Adenosine Triphosphate is the energy currency of the cell. glycogen and triglycerides are broken down in cells to produce ATP
12: Explain each of these systems and the type of exercise each system is typically used for, as well as the period of use:
ATP-PCr system: This system assists in rapidly regenerating ATP from ADP and P. It breaks the chemical bonds between creatine (cr) molecules and phosphate (P) molecules that are already joined in a phosphocreatine (PCr) molecule.
Glycolytic pathway: When energy demands are high and persist beyond ten seconds, your PCr stores begin to deplete and the glycolytic energy system takes the brunt of the work in regenerating ATP.
Oxid phosphorylation pathway: As maximal exercise activity persists beyond 80-90 seconds, intensity must decrease. At this point, you’re forced to slow down. However, if you continue to exercise moderately, oxidative phosphorylation comes to the rescue. As long as oxygen can be utilized, this pathway can continue indefinitely.
13: Name 2 main reasons carbs are important in energy transfer
First, they provide the fastest-acting macronutrient source for energy transfer, especially in the CNS. Second, their storage in the body is quite limited.
14: Describe the 4 key functions of fatty acids and triglycerides
Structural role in cellular plasma membranes.
Endocrine regulation
Essential for fat-soluble vitamins
Efficient bulk energy storage
15: What is the function of amino acids in the body, and what is their significance?
The amino acids that constitute proteins are accountable for everything from the structure (muscle, hair, and nails) to hormones, enzymes, immune components, genetic material, and more.
16: 1 Large Calorie (kcal) is equal to _ 1000 ____calories (cals)
How would you use Large calories (kcals) for food?
When it comes to food Calories, we usually mean large C or kilocalories
17: Why is it unreliable to use calorie counting?
Calorie counting is not accurate because it cannot be accurately calculated due to a plethora of limiting factors and variables
18: List the determinants that provide to the changes in calorie counting
Resistant starches/fibers
Data are outdated Analytical methods imprecise
Product Variety
Soil and growing conditions
Ripeness at the time of harvest
Animals’diets
Length of storage
Preparation/method and cooking time
19: Describe these:
basal metabolic rate: The minimum energy required to maintain the body’s life function at rest
resting metabolic rate: The amount of energy (calories) required to efficiently perform a vital bodily function
thermic effect of feeding: How metabolism responds to the digestion of food and the uptake of nutrients in the blood.
Exercise activity: Physical activity that is performed to become stronger and healthier.
Non-exercise activity thermogenesis: Spontaneous physical activity, things like tapping feet and moving hands.
20: Describe what total daily energy expenditure (TDEE) is
A summation of all things your body does in both active and resting states to burn calories within a day.
21: Which calculation is determined by TDEE?

22: Describe energy balance and the elements that come into play aside from nutrition and fitness
Energy balance is the ratio of calories in vs. calories out. Other elements include individual environmental factors. Genetic factors. Hormonal responses. Digestive/absorptive capacity
23: How is a stable energy balance maintained?
Through purposeful exercise and controlled energy intake.
If you want assistance wrapping your head around this material, make sure to check out Trainer Academy for some awesome ISSA study materials. They have Practice tests, flashcards, audio study guides, and much more.

 Have a question?
Have a question? 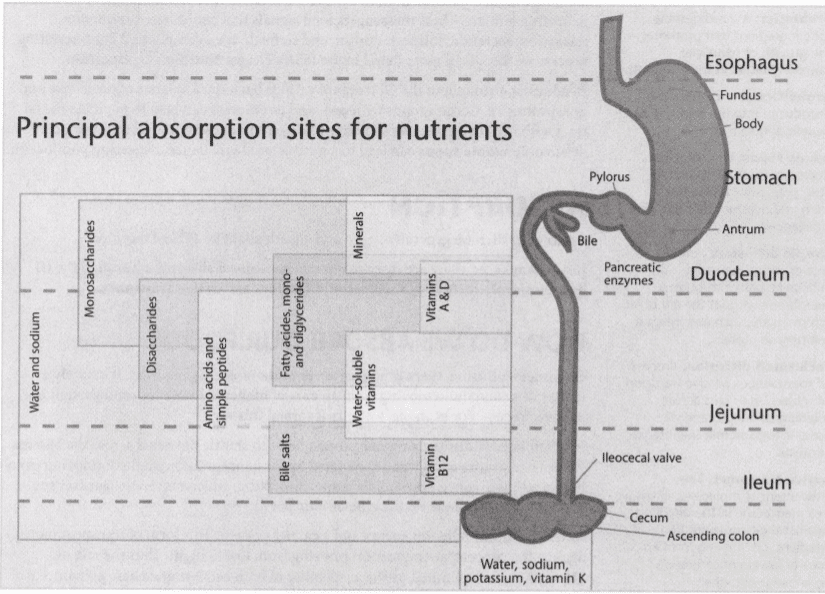




Tyler Read
PTPioneer Editorial Integrity
All content published on PTPioneer is checked and reviewed extensively by our staff of experienced personal trainers, nutrition coaches, and other Fitness Experts. This is to make sure that the content you are reading is fact-checked for accuracy, contains up-to-date information, and is relevant. We only add trustworthy citations that you can find at the bottom of each article. You can read more about our editorial integrity here.