If you have not yet signed up for the ISSA CPT certification, receive a big discount here.
Get your copy of the ISSA CPT exam cheat sheet.
It helps immensely in your ability to study for the ISSA test. This PDF printable one-page sheet gives you a breakdown of the skills and knowledge candidates need to pass the exam.
My PTP students report cutting their ISSA study time and effort in half with Trainer Academy.
Benefit from the Exam Pass Guarantee and Retake Fee Guarantee. Plus, take advantage of my current discount code PTPJULY for 45% off the MVP Program (Ends July 15th, 2025).
Try it out for free here to see if it’s right for you, or read my detailed review for further insights.
1: What is the musculoskeletal system?
The body system responsible for biomechanical action and comprises skeletal muscle groups, connective tissue, and bone/skeleton.
2: What are the 4 functions of the skeletal system in our body?
- Structural Integrity/Biomechanical Function
- Production of blood
- Storage of fat and minerals
- Organ Protection
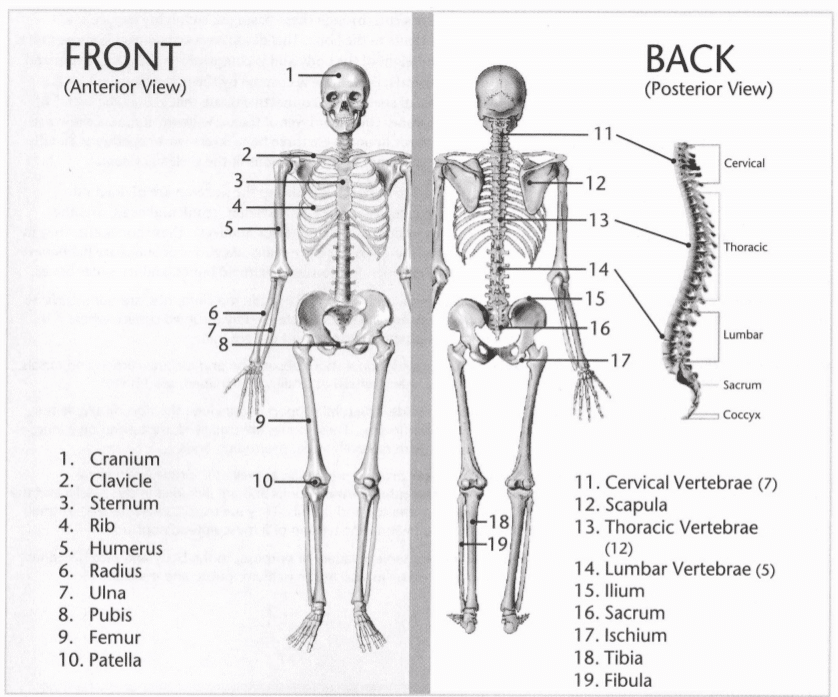
3: What is the total number of bones in the following:
- Overall skeletal system: 206
- Axial skeleton: 80
- Appendicular skeleton: 126
5: What are the three layers that constitute the bone?
Compact, cancellous, osteoblast
6: What are the five bone categories?
Flat, long, short, irregular, and sesamoid
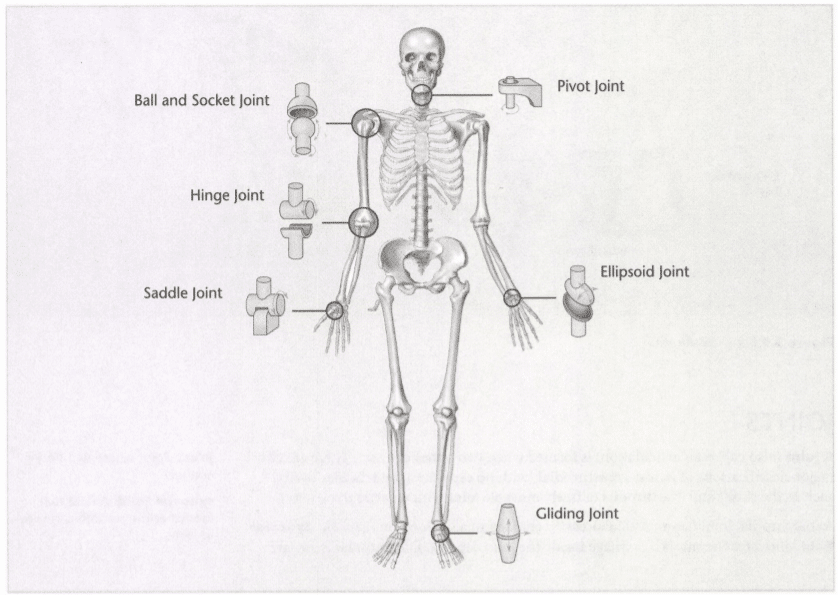
7: What are the 6 joint categories?
Pivot, hinge, saddle, plane, condyloid, and ball-and-socket
8: Label the joints in this chart
9: What is a “tendon?”
Fibrous connective tissue joins muscle to bone.
10: What is a”joint?”
The separation between two or more corresponding bones is configured to allow appropriate movement and is connected by ligaments.
11: Explain the role of the muscular system in our bodies
Move and maintain position
Exclusive PTP CPT Offers |
||
|---|---|---|
Most Popular Cert | Best Online NCCA Cert | Best Study Materials |
Gold Standard Cert | A Good Option | Best CPT for you?  |
12: What are the 3 types of muscles in the body?
- Skeletal
- Cardiac
- Smooth
13: Fill in the chart below:
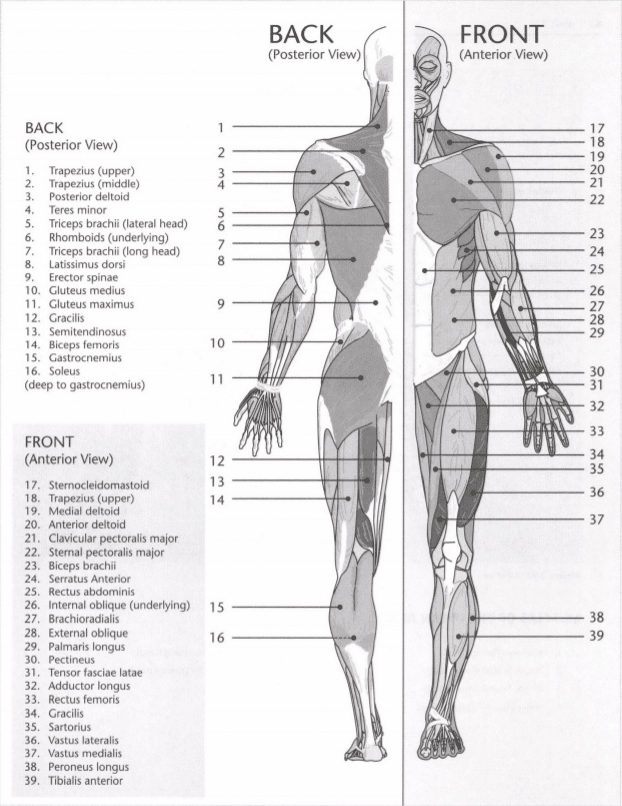
14: Fill in the following diagrams:
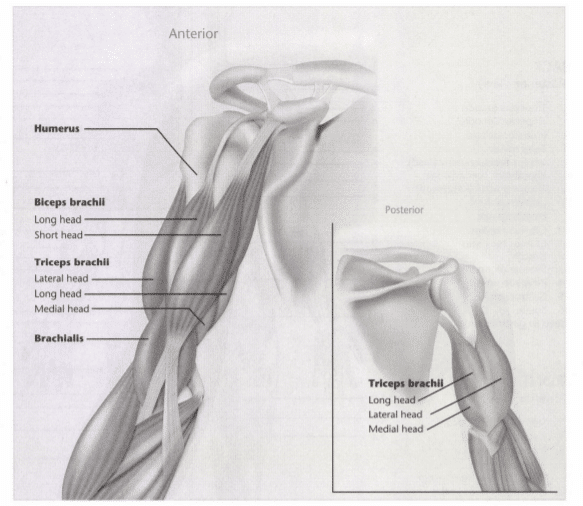
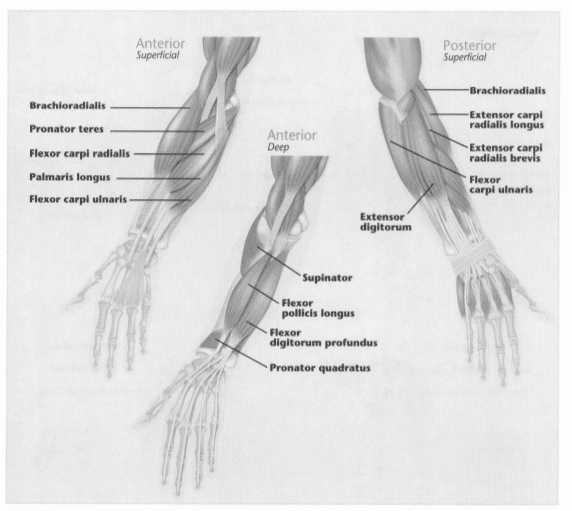
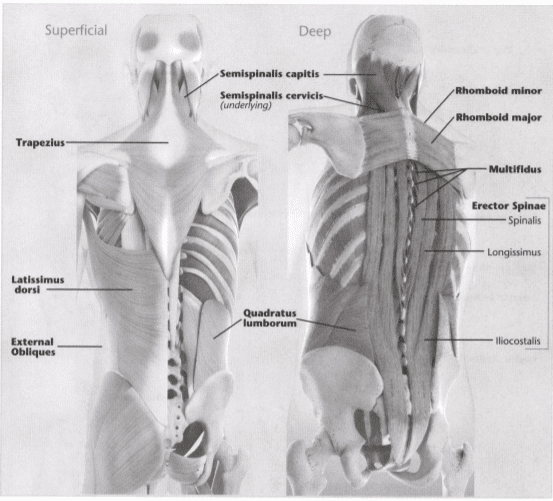
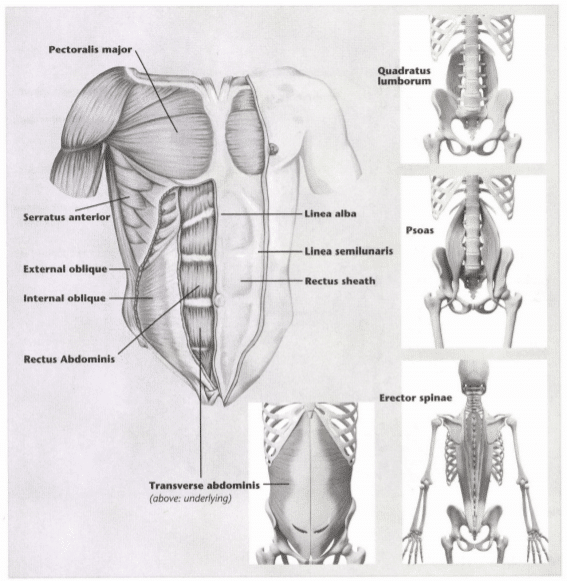
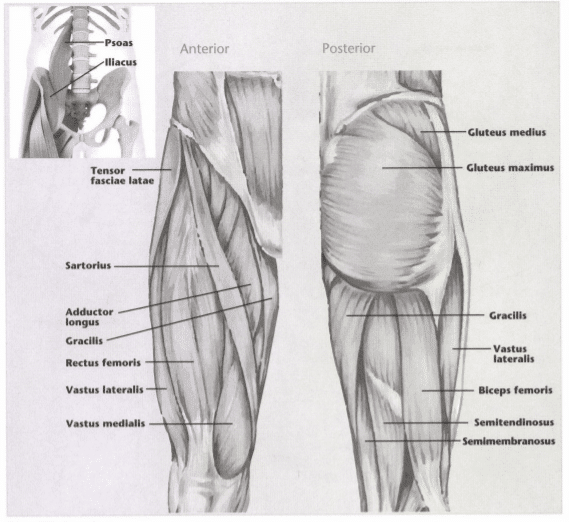
15: What is”origin?”
Origin is the fixed attachment point of muscle to the bone via tendon connection
16: Define “insertion.”
Insertion is a dynamic attachment point of muscle to the bone via tendon and changes with muscle contraction
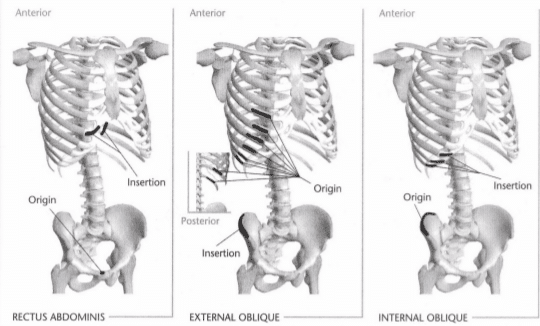
17: Mark the insertion and origin of the rectus abdominis muscle
Indicate origin with an “O” and insertion with an “I.” Indicate the intended action on the line provided below.
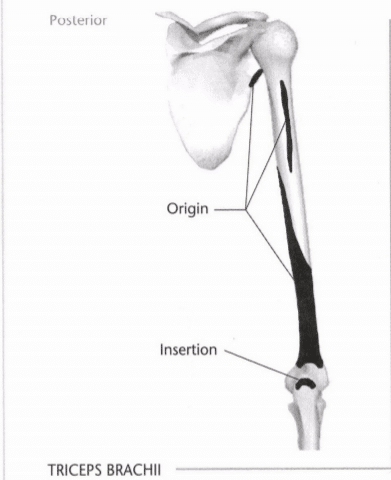
18: Mark the insertion and origin of the triceps brachii muscle
Indicate origin with an “O” and insertion with an “I.” Indicate the intended action on the line provided below. (Hint Refer to Unit 8 if you have trouble with the intended action.)
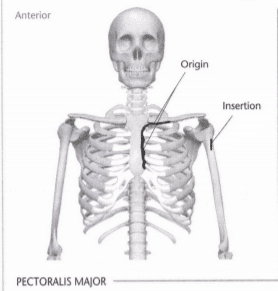
19: Mark the insertion and origin of the pectoralis major muscle
Indicate origin with an “O” and insertion with an “I.” Indicate the intended action in the line provided below. (Hint: Refer to Unit 8 if you have trouble with the intended action.)
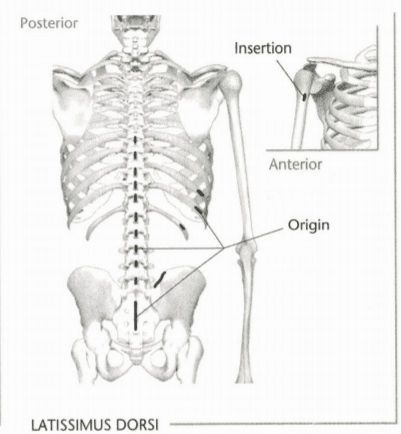
20: Mark the insertion and origin of the latissimus dorsi muscle
Indicate origin with an “O” and insertion with an “I.” Indicate the intended action in the line provided below. (Hint; Refer to Unit 8 if you have trouble with the intended action.)
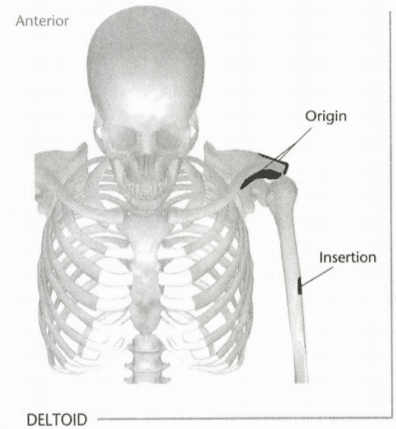
21: Mark the insertion and origin of the deltoid muscle
Indicate origin with an “O” And insertion with an “I.” Indicate the intended action in the line provided below. (Hint: Refer to Unit 8 if you have trouble with the intended action.)
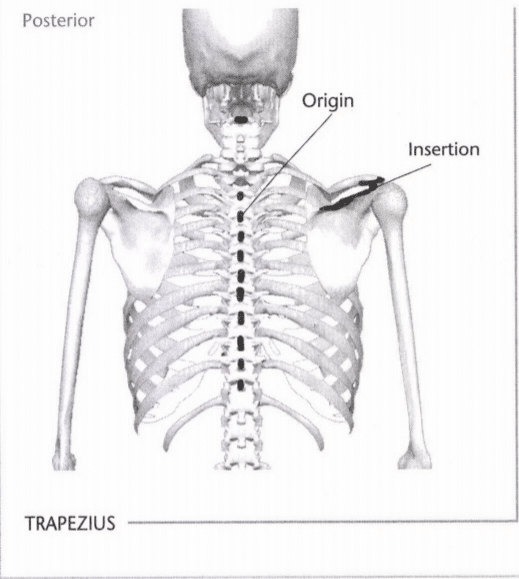
22: Mark the insertion and origin of the trapezius muscle
Indicate origin with an “O” And insertion with an “I.” Indicate the intended action in the line provided below. (Hint: Refer to Unit 8 if you have trouble with the intended action.)
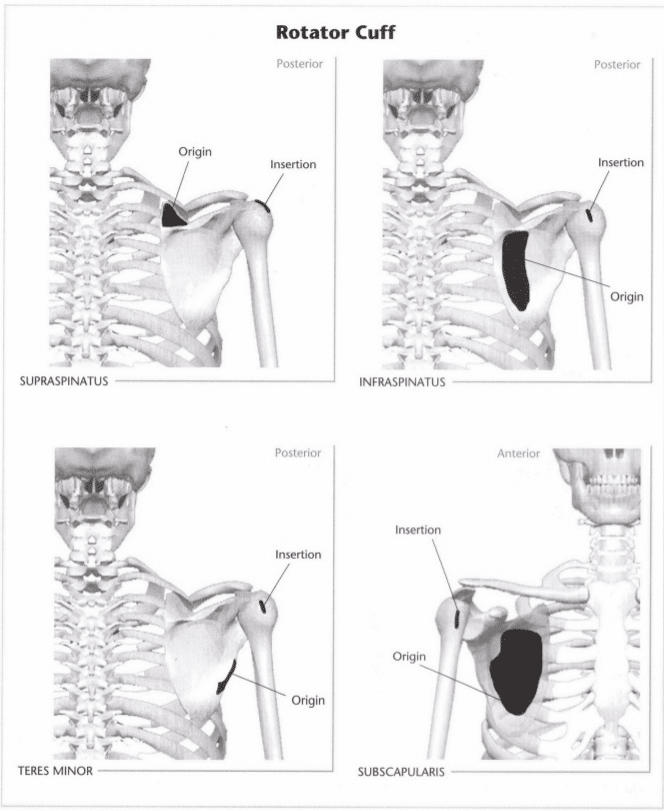
23: Mark the insertion and origin of the rotator cuff muscles
Indicate origin with an “O” and insertion with an “I.” Indicate the intended action in the line provided below. (Hint: Refer to Unit 8 if you have trouble with the intended action.)
24: Mark the insertion and origin of the quadriceps muscles
Indicate origin with an “O” and insertion with an “I.” Indicate the intended action in the line provided below. (Hint: Refer to Unit 8 if you have trouble with the intended action.)
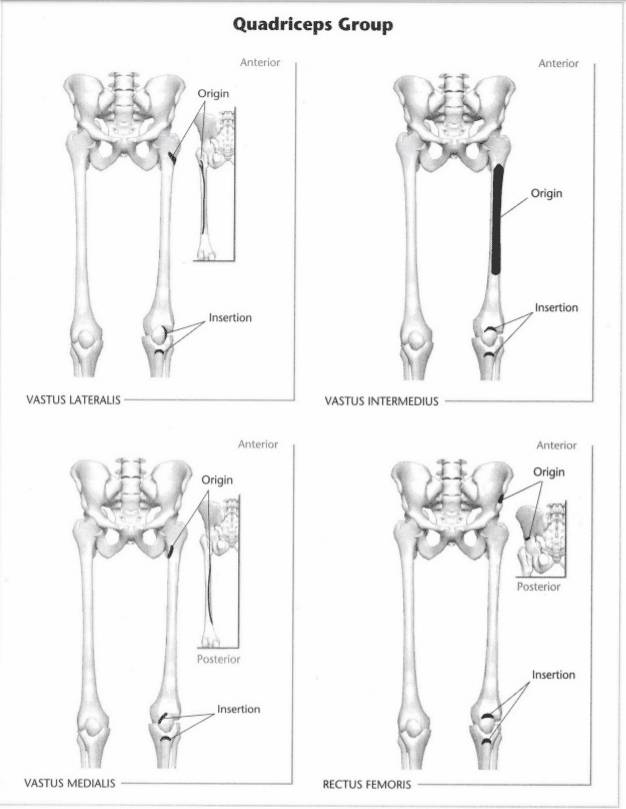
intended action: hip flexion, knee extension
Muscle: Vastus medialis
intended action: Knee extension
Muscle: Vastus lateralis
intended action: knee extension
Muscle: Vastus intermedius
intended action: knee extension
25: Mark the insertion and origin of the hamstring muscles
Indicate origin with an “O” and insertion with an “I.” Indicate the intended action on the lines provided below. (Hint: Refer to Unit 8 if you have trouble with the intended action.)
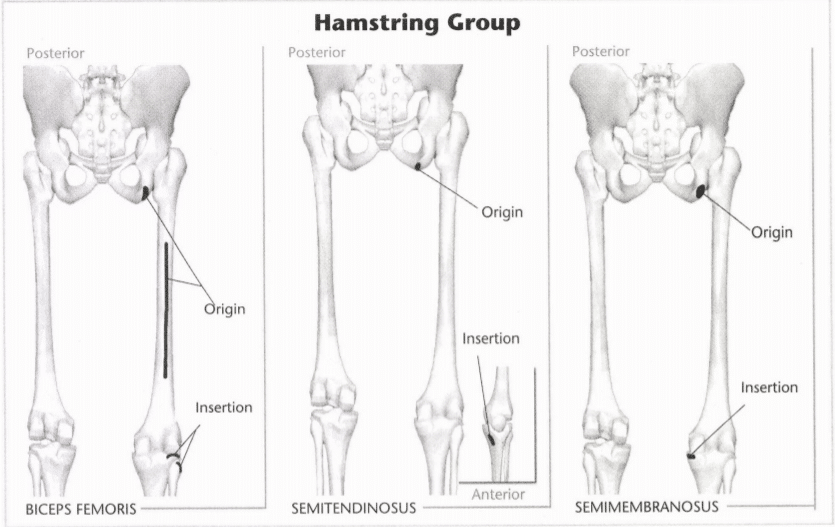
intended action: Extension of the hip, flexion of the knee, internal rotation of the knee
Muscle: Semitendinosus
intended action: Extension of the hip, flexion of the knee, internal rotation of the knee
Muscle: Semimembranosus
intended action: Extension of the hip, flexion of the knee, internal rotation of the knee
26: Complete the chart below to explain skeletal muscle contraction

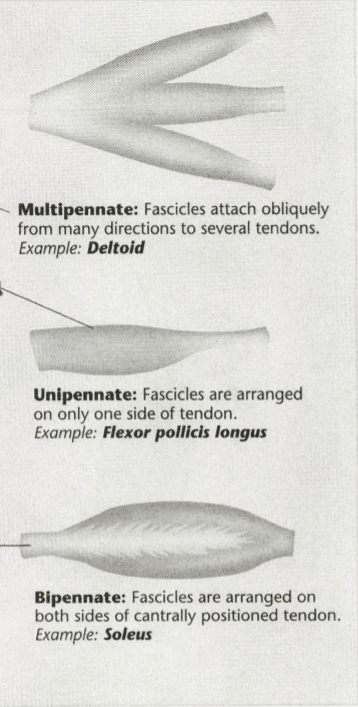
27: What are the six major muscle fiber arrangements?
- Fusiform arrangement
- Upennate
- Bipennate
- Multipennate
- Triangular
- Parallel
28: Determine the muscle fiber arrangements below with examples.

29: What are the 4 categories of muscle fiber types and their nature?
Type I, Type IIa, Type IIx, and Type IIc
30: What is hypertrophy about the training effect?
Hypertrophy is the anabolic response of muscle protein synthesis catalyzed by resistance training or a general adaptation to increased mechanically resistive forces in daily life. It results in increased muscle mass.
If you want assistance wrapping your head around this material, make sure to check out Trainer Academy for some awesome ISSA study materials. They have Practice tests, flashcards, audio study guides, and much more.

 Have a question?
Have a question? 



Tyler Read
PTPioneer Editorial Integrity
All content published on PTPioneer is checked and reviewed extensively by our staff of experienced personal trainers, nutrition coaches, and other Fitness Experts. This is to make sure that the content you are reading is fact-checked for accuracy, contains up-to-date information, and is relevant. We only add trustworthy citations that you can find at the bottom of each article. You can read more about our editorial integrity here.