
If you have not signed up for NASM CPT, sign up here to save 25% with my personal code PTP25.
Get your copy of the NASM CPT exam cheat sheet. It helps immensely in studying for the exam.
My PTP students report cutting their NASM study time and effort in half with Trainer Academy.
Benefit from the Exam Pass Guarantee and Retake Fee Guarantee. Plus, take advantage of my current discount code PTPJULY for 35% off the MVP Program (Ends July 21st, 2025).
Try it out for free here to see if it’s right for you, or read my detailed review for further insights.
Chapter 6 NASM study guide
Guidelines for Health and fitness professionals
What shouldn’t be done
- Counseling clients
- Diagnosing conditions or injuries
- Rehab or physical therapy
- Providing meal plans or detailed diets
What should be done
Exclusive PTP CPT Offers |
||
|---|---|---|
Most Popular Cert | Best Online NCCA Cert | Best Study Materials |
Gold Standard Cert | A Good Option | Best CPT for you?  |
- You should coach clients
- You should identify your client’s limits and past injuries
- Recommend a physician for medical advice
- You can provide general knowledge on nutrition but should refer to a nutritional list or dietitian for more specific needs.
Objective and subjective information
Before starting a routine with any new client, you must assess their current and past health and fitness levels. For subjective information, you need to ask them questions; for objective information, you need to perform fitness assessments.
Objective information:
- Blood pressure
- Cardio assessments
- Postural assessments
- Performance assessments
- Body analysis
Subjective information:
- Clients occupation
- Hobbies, general diet, and lifestyle
- Personal information
- A brief medical history
PAR-Q (physical activity readiness questionnaire)
The PAR-Q was created to help get specific answers on the health history of a new client. This helps determine possible risks of training with a client. If a new client answers yes to any of the questions on the PAR-Q, they will need their doctor’s written permission to start training with you. You can check out the PAR-Q here.
Your client’s occupation
Asking a new clients about their occupation can help determine many postural problems they may be experiencing. Here are some of the most common ones.
- Excessive sitting can cause rounding of the upper back and tight hip flexors.
- Wearing high heels excessively can cause tightness in the muscles of the calves.
- Repetitive overhead movements experienced by construction workers, volleyball players, or electricians can cause impingement in the shoulders.
- An upper crossed syndrome can be caused by stress due to shortening the upper trapezius and scalenes.
Your clients’ lifestyle
This gives the trainer insight into the likes and dislikes of their client. Active recreational activities can be added to the client’s cardio training program.
Your client’s medical history
- Any medications a client takes may affect how intense the exercises should be.
- Chronic diseases need to be accounted for in all exercises and programs.
- Past surgeries may limit your client’s range of motion or may cause joint instability.
- Pain should be accounted for and taken into consideration for all exercises.
- Your client’s medical history will allow you to gauge the risk for any health-related issues your client experiences.
Common medications and heart rate/blood pressure
- Beta-blockers
- Calcium channel blockers
- Digitalis
- Thyroid medications
- Diuretics
- Nitrates
- Bronchodilators
- Vasodilators
- Antidepressants
Note that educating your client on using these medications is not your job. We need to know the basic functions and how they can affect our training regimen with our clients.
Blood pressure and heart rate assessments
The two most common ways of recording heart rate are using the radial pulse on the thumb side of the wrist (preferred method) or the carotid pulse on the side of the neck (use with caution).
Blood pressure can be measured using a sphygmomanometer with a pressure dial, inflatable cuff, stethoscope, and a bulb with a valve. It is highly recommended that personal trainers take a professional course for taking blood pressure.
Exclusive PTP CPT Offers |
||
|---|---|---|
Most Popular Cert | Best Online NCCA Cert | Best Study Materials |
Gold Standard Cert | A Good Option | Best CPT for you?  |
https://exrx.net/Testing/HeartRate has all the blood pressure and heart rate assessments.
Target heart rate zones and the formula for maximum heart rate
The predicted maximum heart rate equation is 220-age. Multiply this number by the training zone (between 65% and 95%) of the predicted heart rate Max.
Training zone 1: This helps to build your client’s aerobic base and will aid in recovery.
Training zone 2: This helps to build your client’s aerobic endurance.
Training zone 3: This helps your client build high-end work capacity (primarily anaerobic).
Body composition assessments
- Underwater weighing: The most accurate way of measuring body composition. It measures the mass per unit volume of the human body.
- Bioelectrical impedance: The most convenient way to measure body composition. Also known as body fat analysis. It analyzes the strength and the speed of an electrical impulse sent through the body. With the addition of information such as gender, weight, and height, it can relatively accurately predict body fat percentage.
- Skinfold tests: The most difficult way to measure body fat. A skinfold caliper can measure the width of external body fat in millimeters. You measure different sites on the human body, and the grand total is added up to create a body composition total. Here’s a great site on how to take skinfold measurements.
Circumference measurements
Circumference measurements help to measure the circumference of different body parts. Some of the benefits of circumference measurements are: it’s easy to do, provide quick information on client progress, are affordable, and are not hard to learn the technique. Here is a good resource for circumference measurements.
Suggested circumference measurement areas:
- Upper arms
- Neck
- Calves
- Chest
- Thighs
- Hips
- Waist
- Forearms
BMI (Body mass index)
The body mass index test is extremely easy and is a good way to screen patients and it applies to both men and two women. Body mass index is difficult to apply to people with excessive muscle mass, such as bodybuilders. Here are the ranges for body mass index. Here’s a good site to calculate BMI.
Formula: Weight (kg) / Height (m2)
- <18.5 = Underweight
- 18.5 to 24.9 = Healthy
- 25 to 29.9 = Overweight
- 30 to 34.9 = Obese
- >35 = Severe obesity
- ≥ 40 = OMGG
YMCA three-minute step test
This test calculates your client’s cardiorespiratory fitness level and efficiency. It is done in a time of only three minutes, which makes it extremely easy to do. You will need a 12-inch step to perform this test.
- Have your client step up and down the step at a pace of 96 steps per minute.
- Having a metronome to have your client follow along with as they step up and down is handy.
- After three minutes of stepping, you must immediately find the recovery pulse.
- Depending on this pulse, you will start your client in the appropriate heart rate training zone according to the text.
The Rockport walking test
This is another cardiorespiratory assessment to assess your client’s cardiovascular fitness. This test is best for obese clients.
- Jot down your clients’ wait and have them walk 1 mile on the treadmill as fast as he or they can control.
- Record the time it took for your client to go 1 mile and record their heart rate the exact second that they finish the 1 mile.
- Weight in pounds = 1 for men and 0 for women. The time is expressed in minutes and the 100th of minutes. Heart rate is in beats per minute and age is in years.
- The formula is located on page 131 in the textbook. You do not need to memorize this formula; recognize it as being the formula for the Rockport walk test.
Pronation distortion syndrome
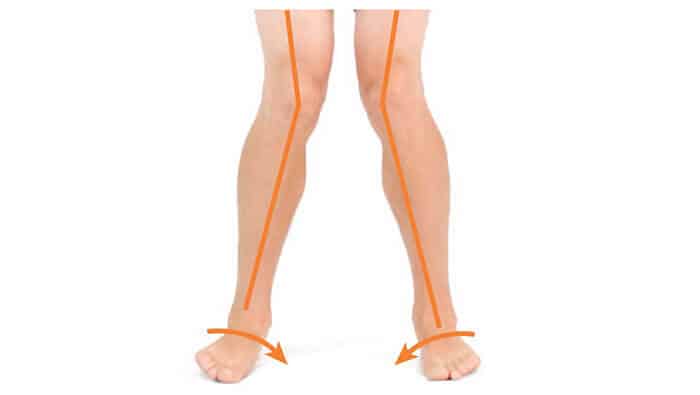
This is characterized as having flattened feet and abducted knees. This can lead to pain in the lower back/lower extremities and injuries. It is very common for ACL injuries.
Lower crossed syndrome
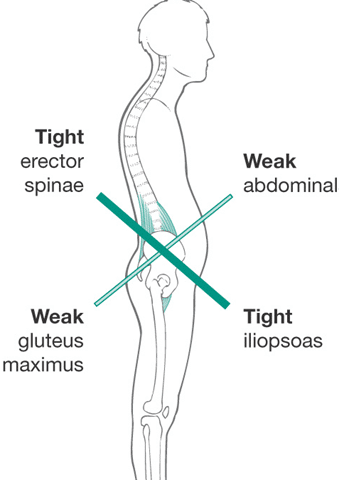
An anterior pelvis or lower back tilt characterizes this postural distortion syndrome.
Upper crossed syndrome
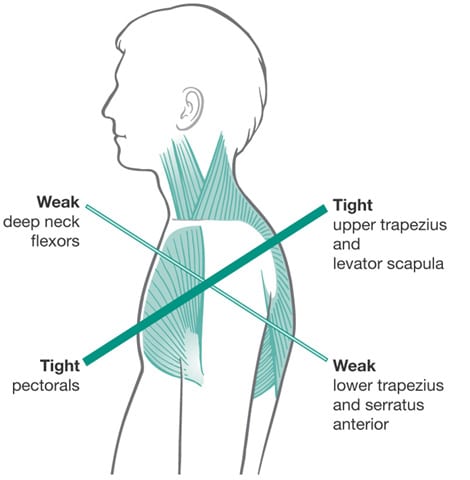
A forward head posture and rounded shoulders characterize this.
The overhead squat assessment
MEMORIZE THE FULL THING! Especially the chart on page 144!
If you want additional study materials, check out the team over at Trainer Academy. They have incredible study materials for NASM And I have a special limited-time discount for my readers. I also suggest you check out my review on Trainer Academy here.

 Have a question?
Have a question? 



Hi Tyler,
I was wondering due to financial constraints, if I was to study your free study guides that are provided and use your study techniques, is it possible to get a passing grade and even pass with flying colors on the test? Or is it suggested to try and get your study guides?
Hey there, you can definitely pass the exam using my study guide and studying the textbook extensively. I do typically recommend a practice exam for 2 for the National Academy of sports medicine. Good luck with your personal training career.
Hi Tyler, I just wanted to point out an important typo for pronation distortion syndrome on this page. The textbook has this defined with adducted and internally rotated knees, not abducted like it’s been written here.
Otherwise, thanks a lot for all your hard work! This site has really been helping me!
Hey Brian, thank for pointing this out and I will definitely change this. How is the studying for the NASM exam going?
Hey man i stumbled upon your video of the 10 tips to studying for CPT NASM Exam and ive been killing myself trying to memorize everything but dont have any sort of knowledge on how to even start to do it the right way. Your website is very legit and user friendly and makes me understad key things the book does a horrible job at. is there a way you can recommend what i should do? like should i read your study guide first then memorize the flash cards, or should i memorize the study guide then memorize the flashcards. Im very lost and need help and you seem to be the man with the plan. Please E-mail me the answer and if you do i want to thank you because im so lost and confused and its killing my vibe for the whole thing!
Hey James, I definitely recommend going through the entire study guide on my website as well as all of the flashcards and practice exams. But to be honest, I do not cover everything and it is just meant to be a brief overview of some of the more important topics that you should be studying. If you are worried about passing the exam for the National Academy of sports medicine I definitely recommend checking out Trainer Academy. They have some excellent study materials and even provide an exam pass guarantee.
How can you see the right or wrong answers rather than just your score? Can you view them?
Hello,
At this point in time I do not have an answer sheet live on my website. I will work on getting all of the test answers in quizzes so that people can double check their answers on my website. Thanks for the suggestion.
Hey Tyler I’m very into being a fitness trainer can you tell me how if I become nasm certified how to properly look for jobs a gym & how to get clients
Yes, I have some specific articles on what to do after you have your personal training certification. There are a lot of different tactics to get work and to succeed as a trainer.
Hi Tyler! Love your website… been so helpful as I have been studying. Just wondering, is there a PDF or printer friendly version of your free study guide? I love your study guide, but really like having a paper copy of my study materials. Please let me know! Thanks!
Hey Heather, as of right now I do not have a PDF version of the free study guide but thanks for the recommendation and I think that would be a great addition for people!